Table Of Content
This can lead to poorly-informed decisions if leadership doesn’t ask for input or feedback from their project team. Making critical decisions and overseeing the product development process from conception to market introduction is part of product management. The top-down approach relies on higher authority figures to determine larger goals that filter down, while the bottom-up approach gives all team members a voice in decision-making. Top-down prioritizes high-level planning, and bottom-up emphasizes executing individual tasks. Adopting Kumospace in your organization can aid in establishing a balanced management approach, promoting teamwork, innovation, and a sense of ownership among team members.
The Power of Bottom–Up Design in Software Development
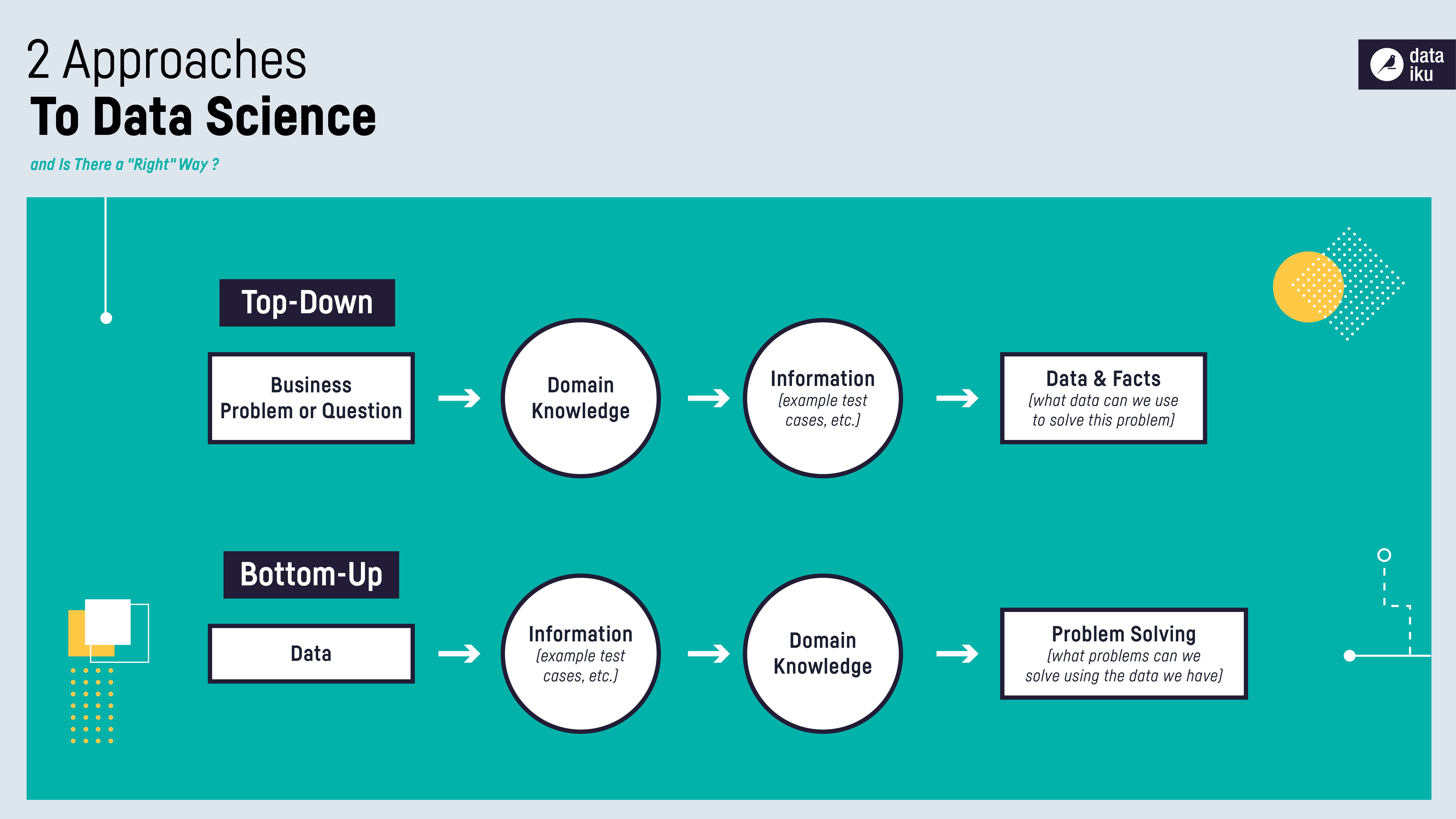
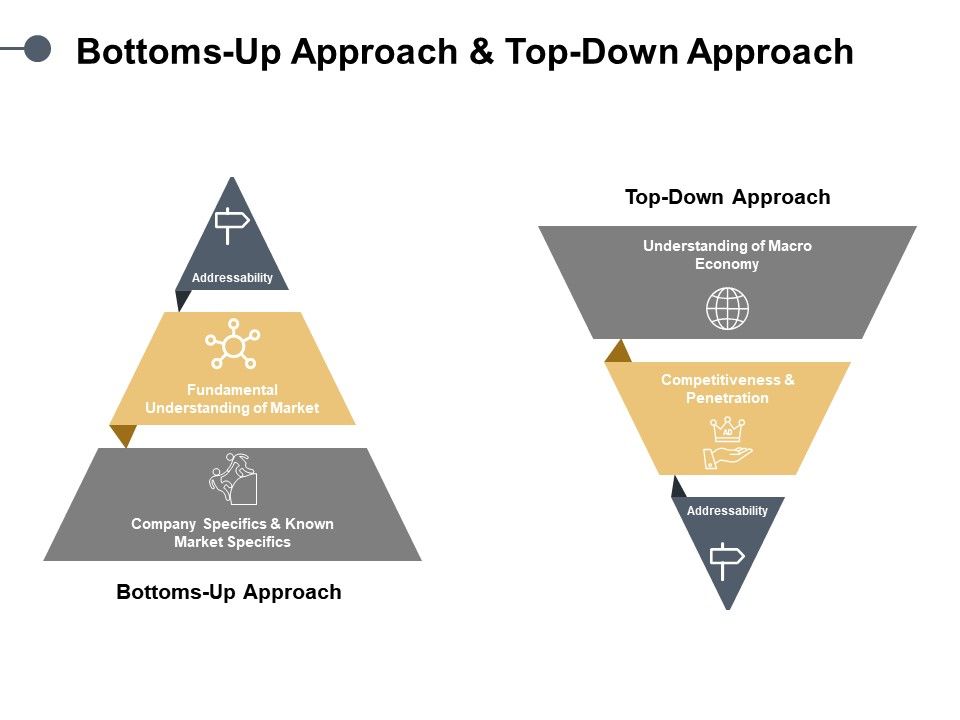
In the financial world, analysts or whole companies may be tasked with focusing on one over the other, so understanding the nuances of both is important. The top-down approach and bottom-up approach are the algorithm design methods where top-down is a conventional approach which decomposes the system from high-level specification to low-level specification. On the other hand, the bottom-up approach is more efficient and works in an inverse manner where the primitive components are designed at first then proceeded to the higher level. Top-down approach and bottom-up approach are two different management styles that have their own advantages and disadvantages. Depending on your situation, you may need to use one approach more than the other, or balance them both.
Difference Between Top-down and Bottom-up Approach
If there are not enough resources or producers in the ecosystem, there is not enough energy left for the rest of the animals in the food chain because of biomagnification and ecological efficiency. An example would be how plankton populations are controlled by the availability of nutrients. Plankton populations tend to be higher and more complex in areas where upwelling brings nutrients to the surface. Parsing is the process of analyzing an input sequence (such as that read from a file or a keyboard) in order to determine its grammatical structure. This method is used in the analysis of both natural languages and computer languages, as in a compiler.
What is Dynamic Programming? Top-down vs Bottom-up Approach - Simplilearn
What is Dynamic Programming? Top-down vs Bottom-up Approach.
Posted: Wed, 01 Mar 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Boost Employee Performance with Workplace Wellness Programs in 2024
As unforeseen events pop up during projects, targets are shifted through the open line of communication between business executive and lower-ranking employees. Collaboration fostered through the bottom-up approach gives businesses the transparency needed to maintain successful processes. In this case, a business invites the entire team to participate in the company’s management and decision-making process. Communication and an all-encompassing approach is a vital aspect of this style of management, lending itself to the appropriate name of bottom-up communication.
More informed decisions
Top-down investing is often easier for new investors who are less experienced at reading a company's financial statements and for those who don't have the time to analyze those financials. This strategy is sometimes referred to as “inductive reasoning,” and the word “synthesis” refers to the final product. When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. It is common for populations to be influenced by both types of control, and there are still debates going on as to which type of control affects food webs in certain ecosystems.
How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes
The open communication and shared solutions among all employees ensure that projects remain fluid and goals are achieved in a timely fashion. There are many industries in the workforce that find this business approach especially appealing. In particular, designers, software developers, and engineers are drawn to the top-down policy because reverse product engineering often leads to the best final outcome.
Advantages of bottom-up management
Since all decisions are made at the top, a mismatched project management hire can have a bigger impact on the success of the team. Many process problems are only visible at the lower level, so project managers who fail to solicit feedback from individual team members before making decisions can inadvertently cause significant problems, delays, and losses. The top-down approach results in clear, well-organized processes that leave little room for confusion. Because all decisions are made in one place and all communication flows in one direction, mix-ups and misunderstandings happen less frequently than with other management styles. A more modern management technique, the bottom-up approach developed concurrently with a shift in focus towards Industrial and Organizational Psychology (I/O). The field of I/O encourages employers to consistently value their employees and make their contributions to the company a top priority.
Top-down approach vs. bottom-up approach: What’s the difference?
They further refine the view to a particular sector, and then to the individual companies within that sector. The top-down approach emphasizes on the isolation of the submodules (signifies the low coupling between the modules) while ignores the identification of communication and reusability concept. While in the bottom-up approach, information hiding and reusability are the prominent factors. Thus, the top-down method begins with abstract design and then sequentially this design is refined to create more concrete levels until there is no requirement of additional refinement.
The flow of the bottom-up approach:
Historically, discretionary stocks are known to follow economic cycles, with consumers buying more discretionary goods and services in expansions and less in contractions. An analyst seeking a top-down perspective wants to look at how systematic factors affect an outcome. In corporate finance, this can mean understanding how big-picture trends are affecting the entire industry. In budgeting, goal setting, and forecasting, the same concept can also apply to understand and manage the macro factors. The top-down approach is often used in situations where there is a need for speed, efficiency, consistency, and control. For example, when launching a new product, implementing a change, or dealing with a crisis.
By integrating both strategies, product managers can create an all-around product vision and strategy that balances business objectives with the needs of the users. To build products that meet the target market’s needs and drive business success, product teams need to comprehend the pluses and minuses of both strategies. Top–down is a programming style, the mainstay of traditional procedural languages, in which design begins by specifying complex pieces and then dividing them into successively smaller pieces. The technique for writing a program using top–down methods is to write a main procedure that names all the major functions it will need.
Bottom–up approaches, in contrast, use the chemical properties of single molecules to cause single-molecule components to (a) self-organize or self-assemble into some useful conformation, or (b) rely on positional assembly. These approaches use the concepts of molecular self-assembly and/or molecular recognition. Such bottom–up approaches should, broadly speaking, be able to produce devices in parallel and much cheaper than top–down methods but could potentially be overwhelmed as the size and complexity of the desired assembly increases. Next, we examine how factors such as company size, structure, culture, and industry affect the choice of management approach.
Both approaches have their advantages and challenges, and understanding these nuances can help organizations choose the most effective management style. A bottom–up approach is the piecing together of systems to give rise to more complex systems, thus making the original systems subsystems of the emergent system. Bottom–up processing is a type of information processing based on incoming data from the environment to form a perception. In a bottom–up approach the individual base elements of the system are first specified in great detail.
In fact, bottom up management styles have become increasingly popular in these fields. Bottom-up management, on the other hand, provides several benefits, such as increased employee confidence, enhanced collaboration, and comprehensive project management. By involving employees in the decision-making process, bottom-up management fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to increased motivation and satisfaction. This approach is particularly effective in industries where innovation and collaboration are critical to success, such as software development and product design. This policy type relies on a hierarchy of high versus low rank employees — the high ranking individuals rely on it for the decision of tasks and goals, and the low ranking employees to complete tasks and achieve goals. This structured programming of management leads to neatly defined subsystems of employees and departments.
The Bottom-Up Approach is a kind of integration testing in which the modules at lower levels are tested first with modules at higher levels, and then the modules at higher levels themselves are tested. When it comes down to it, effective managers know how to balance the efficiency of the top-down approach with the collaborative and creative advantages that come from the entire team. When approaching a project from the top down, higher-level decision-makers start with a big picture goal and work backward to determine what actions different groups and individuals will need to take in order to reach that goal.
Similarly, a top-down approach can be implemented in manufacturing organizations to enhance efficiency and agility. By providing clear directives and a unified vision, the top-down approach enables the organization to quickly adapt to changes in the market and maintain a competitive edge. Having outlined the basics of both top-down and bottom-up approaches, let’s consider their respective merits and demerits.
This approach caused upper management to lessen their hold on decision-making power, and instead, allowed for lower ranking employees to contribute more frequently. The processes are streamlined and communicated to lower rank employees, who carry out these tasks. Consequentially, projects are more easily managed, and risk is decreased significantly due to strategic decisions created from the top management. This approach relies on the executive level to decide how to prioritize, manage, and conduct everyday processes. In the software development process, the top–down and bottom–up approaches play a key role. By following these best practices in the management process, organizations can create a management style that leverages the strengths of both approaches, resulting in a more efficient, innovative, and engaged workforce.

No comments:
Post a Comment